You are here 
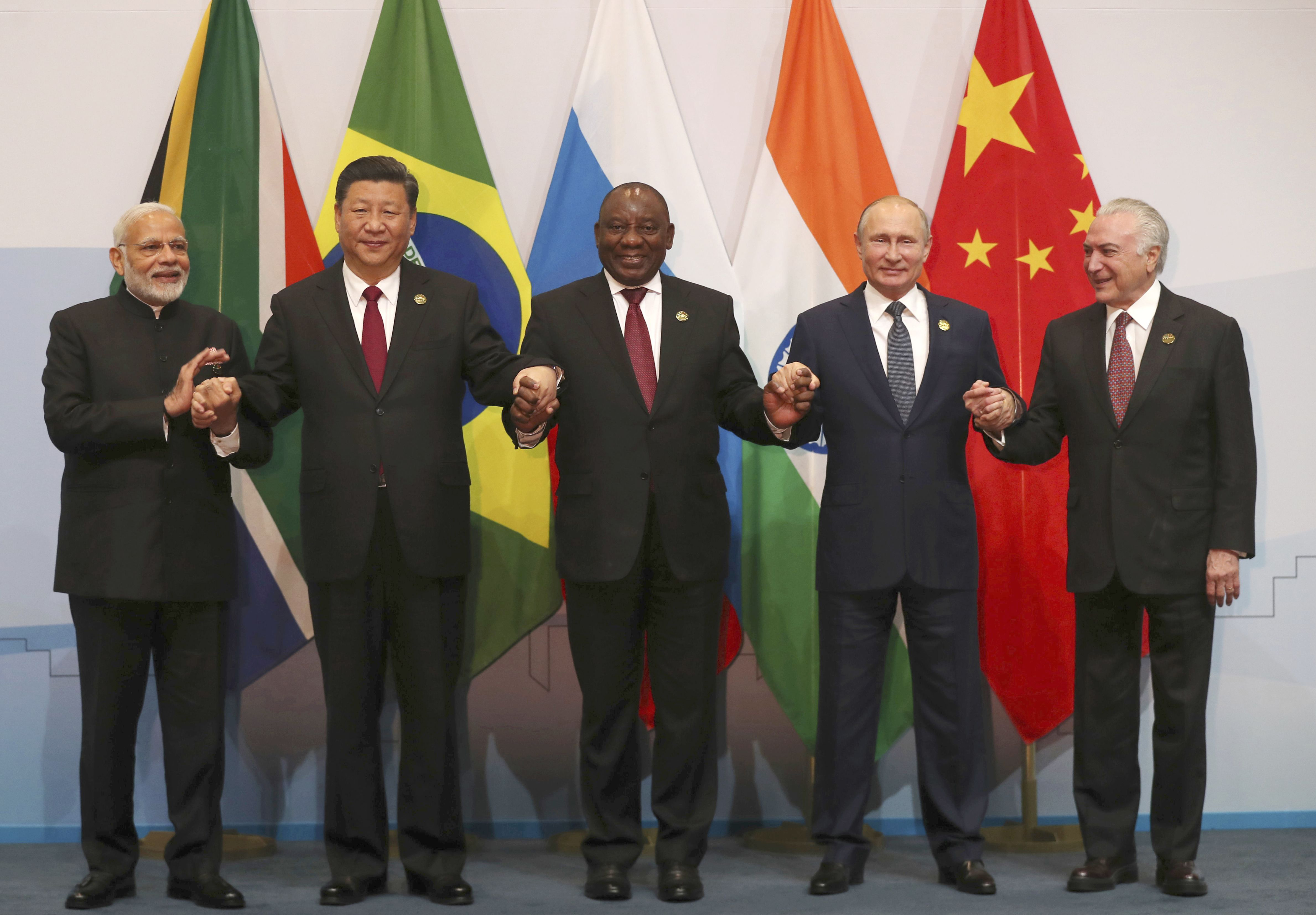






Steadfastly, the BRICS Pact is building a multi-polar society in which economic and political reform enhances the quality of professional services that is expected with wealthier, healthier and cleaner ambitions for the planet. Fittingly, the BRICS Pact is a major economic bloc established between Brazil, Russia, India, China and South Africa and is the undisputed trend setter for balancing global trade as Westernization deteriorates international norms. Presently, the BRICS+ Pact embodies over 46% of the world population as four out of the five states are among the top 10 in world population. Similiarly, BRICS+ nations have an accumulated nominal GDP of over $28 trillion (USD) which is nearly 27% of the gross world product (GWP). Astutely, the BRICS Pact has taken oversight of the de-dollarization process which is achieved with the BRICS payment system while undergoing new framework for a multi-polar world order and global financial system. Centrally, the BRICS Pact is positioned to reduce global dependence of the US dollar which is supported by a mediocre pivot towards Asia.



As mentioned, the BRICS Pact is capitalized with 27% of the gross world product which indicate significant contributions to the global supply chain. Economically, the BRICS Pact is at the helm of establishing the BRICS Security Council to modernize and ensure international security for inter-government cooperation with the global supply chain. Furthermore, formation of the BRICS Security Council includes naval fleet expansion projects for members to extend cooperation with climate security. Meticulously, the BRICS Security Council subsidizes climate security while synchronizing satellite communication systems to regulate the de-dollarization process. Principally, the BRICS Security Council is equipped to safeguard international trade routes during war and peace times. Immensely, the BRICS Security Council is prepared to uphold supply chain economics over extended sanctions, tarrifs, geopolitical tensions, and economic shifts. Similarly, the BRICS Pact is surpassing US dollar reserves held by central banks with a combined foreign reserve total of $5.2 trillion (USD). Mainly, this is attributed to the cryptocurrency flight established from US influence on international monetary policies. Accordingly, the BRICS Security Council prioritizes the de-dollarization process which includes establishing the Strategic Pact Development Program (SPDP - also known as the 5-yr Development Scheme) while building the infrastructure for the Ministry of International Justice.
Politically, the BRICS Pact is intent with outpacing the Western states of Europe and North America through various approaches to the de-dollarization process. Strategically, the BRICS Security Council is devoted to achieving a multi-polar world order while ensuring economic, social and political cooperation towards regional development. Decisively, the BRICS Security Council unifies climate security as demand for next-generation communication networks elevate environmental protection. Particularly, the BRICS Security Council is assigned with wildfire prevention drills which include joint training missions, naval intervention strategies and deep surveillance tactics. Resolutely, the BRICS Security Council is building the technological infrastructure to extend cooperation with field operations which impact climate security, energy exploration and food security.

Extensively, BRICS Central is equipped with the infrastructure to support a multi-polar world order and new financial system which requires a centralized platform for advanced inter-connectivity. Systematically, BRICS Central implements regional development through various payment systems to support an adequate money supply within emerging markets. Essentially, the BRICS Central mission is achieved while yielding to the gold standard which strengthens long-term monetary policymaking. Correspondingly, the BRICS Central mission is sustained through implementation of various services which underscore short-term market trends. Sufficiently, the BRICS Central mission involves using the gold exchange standard as an instrument for extending the money supply beyond the limitations of crypto currency trading. Assertively, the BRICS Pact has moved forward in exploring investment options for a different reserve international currency with the establishment of new international payment systems. Initially, on 24 March 2009, Zhou Xiaochuan, President of the People's Bank of China, demanded for "creative reform of the existing international monetary system towards an international reserve currency." He stated it would "significantly reduce the risks of a future crisis and enhance crisis management capability." Proficiently, the gold standard is applied to standardize exchange rates between currencies of different nations while eliminating external pressures from international trade.
Relentlessly, the BRICS Pact is isolating the G-7 with the de-dollarization process while establishing the framework for a multi-polar world order. Synchronically, rising tensions surrounding US foreign policies accelerate the momentum for new international payment systems. Additionally, the development of high-speed railroads, nuclear power plants and other civil engineering projects increases productivity for emerging markets as BRICS Central heightens regional development. Inseparably, Russia has delivered the Faster Payments System (FPS) to facilitate interbank transfers with more than 200 interconnected banks. Progressively, China has established the Cross-Border Inter-Bank Payments System (CIPS) which governs the exchange of information and financial transactions in a secure, standardized and reliable environment. Candidly, Fang Xinghai, former vice-chairman of the China Securities Regulatory Commission iterated, “Yuan internationalisation is a must to offset external financial pressure. If our overseas assets were held in yuan, there won’t be such worries [over US dollar devaluation].” Moreover, the BRICS Business Council is integrating economic development projects within the following private sectors: agribusiness, digital economy, skills development, infrastructure, manufacturing, aviation and financial services throughout the BRICS+ framework. Precisely, the gold standard is the primary tool for balancing international trade within the framework of rebuilding the global financial system.
 Aptly, the New Development Bank (NDB) was established in 2014 as leaders of the BRICS Pact signed the Fortaleza Declaration. Jointly, the Fortaleza Declaration states, "The Bank (NDB) shall have an initial authorized capital of $100 billion (USD). The initial subscribed capital shall be $50 billion (USD), equally shared among founding members. The first chair of the Board of Governors shall be from Russia. The first chair of the Board of Directors shall be from Brazil. The first President of the Bank shall be from India. The headquarters of the Bank shall be located in Shanghai. The New Development Bank Africa Regional Center shall be established in South Africa concurrently with the headquarters.” Proportionately, the Africa Regional Center (ARC) has established various initiatives and projects of scale which focus on sectors such as: water, transportion, energy and urban development with the Government of South Africa.
Aptly, the New Development Bank (NDB) was established in 2014 as leaders of the BRICS Pact signed the Fortaleza Declaration. Jointly, the Fortaleza Declaration states, "The Bank (NDB) shall have an initial authorized capital of $100 billion (USD). The initial subscribed capital shall be $50 billion (USD), equally shared among founding members. The first chair of the Board of Governors shall be from Russia. The first chair of the Board of Directors shall be from Brazil. The first President of the Bank shall be from India. The headquarters of the Bank shall be located in Shanghai. The New Development Bank Africa Regional Center shall be established in South Africa concurrently with the headquarters.” Proportionately, the Africa Regional Center (ARC) has established various initiatives and projects of scale which focus on sectors such as: water, transportion, energy and urban development with the Government of South Africa.
Concurrently, the New Development Bank (NDB) has established agreements with several national development banks, multilateral development banks, commercial banks and multilateral institutions for mobilizing financial resources to attract new development with global supply chain economics. Equivalently, the NDB embodies the framework to extend interbank networking behind the scrutiny over US sanctions which elevate the growing future risk of cyber terrorism (i.e. coin-o-graphic affects).
Meanwhile, the NDB has scaled regional development with an environmental and social framework for addressing the growing demand in financial instruments which accelerate the de-dollarization process. Expressly, the environmental and social framework governs the use and management of proceeds from green, social and sustainability bonds. Collectively, the NDB is the leading source for expanding interbank networks which include development schemes involving climate security. Systematically, cooperation with climate security generates longer term investment products for energy-based projects that expand interbank networking. Innovatively, the NDB improves regional development as the de-dollarization process includes the establishment of a new international system. Precisely, the Strategic Pact Development Program which is brokered with the BRICS Security Council underscores the race for a new international system.
|
⮱ BSN Network Homepage
|
 |
 1st Quarter |
 2nd Quarter |
 3rd Quarter |
 4th Quarter |
 |